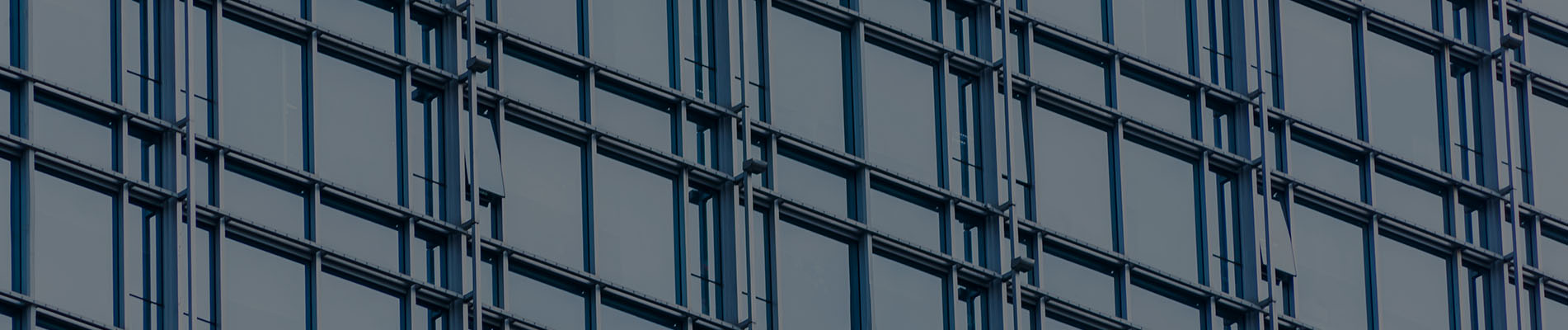
Glass sealant
Glass sealant is a material used to bond and seal various types of glass with other base materials. It is mainly divided into two categories: silicone sealant and polyurethane sealant (PU). Silicone sealant is divided into acid sealant, neutral sealant, structural sealant, etc. Polyurethane sealant is divided into adhesive sealant and sealant.
Specific applications of glass sealant
1. Suitable for weather-resistant sealing of various curtain walls, especially recommended for weather-resistant sealing of glass curtain walls, aluminum-plastic panel curtain walls, and dry-hanging stone.
2. Seam sealing between metal, glass, aluminum, ceramic tiles, organic glass and coated glass.
3. Joint sealing of concrete, cement, masonry, rock, marble, steel, wood, anodized aluminum and painted aluminum surfaces. In most cases there is no need to use a primer.
4. It has excellent weather resistance such as ozone resistance and ultraviolet resistance, and has a long service life.
Sealant introduction
Sealant refers to a sealing material that deforms with the shape of the sealing surface, is not easy to flow, and has a certain adhesive force. It is usually based on dry or non-drying viscous materials such as asphalt, natural resin or synthetic resin, natural rubber or synthetic rubber, and then adds inert fillers, followed by plasticizers, solvents, curing agents, accelerators, etc. Waiting for production. Sealants are distinguished by performance. Their only function is to seal. Weather-resistant sealant, silicone structural sealant, and polyurethane sealant all have sealing functions, but they also have other very important functions, such as high bonding strength and good weather resistance.
Specific applications of sealants
1. According to classification, it can be divided into building sealant, automobile sealant, insulation sealant, packaging sealant, mining sealant and other types.
2. According to the classification after construction, it can be divided into cured sealant and semi-cured sealant. Cured sealants can be divided into rigid sealants and flexible sealants. Rigid sealant is a solid that forms after vulcanization or solidification. It has little elasticity, cannot bend, and usually the joint cannot move; flexible sealant is elastic and soft after vulcanization. Non-curing sealant is a soft-curing sealant that retains its non-drying tackifier and continues to migrate to the surface after application.
Structural sealant
The structural sealant has high strength (compressive strength>65MPa, steel-to-steel positive tensile bonding strength>30MPa, shear strength>18MPa), can withstand large loads, is resistant to aging, fatigue, and corrosion, and has good performance within its expected life. Stable adhesive suitable for bonding structural components that can withstand strong forces.
1. Mainly used for structural or non-structural bonding devices between glass curtain wall metal and glass.
2. The glass can be directly connected to the surface of metal components to form a single assembly component to meet the design requirements of fully hidden frame or semi-hidden frame curtain walls.
3. Structural bonding and sealing of insulating glass.
4. Suitable for bonding, caulking and sealing of porous stone, laminated glass, insulating glass, mirror glass, coated glass, zinc, copper, iron and other materials.
Post time: Nov-02-2023

